|
Vascepa’s Coronary Physiology Impact | Stress & CVD
May 18, 2023
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“You are drinking from a bottle… you are breathing on your own.”
|
|
Two highlights from a coverage denial letter sent by an insurer directly to a baby on its fourth day in a neonatal intensive care unit. If only the baby could read.
|
|
|
Cardiology Pharmaceuticals
|
|
|
|
|
|
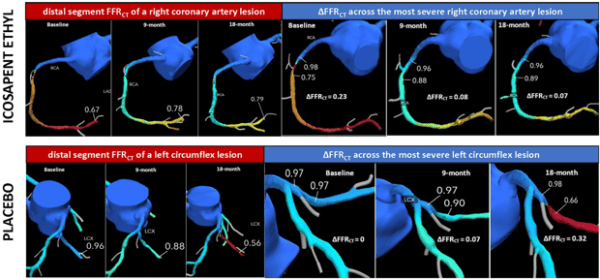
Amarin presented results from the latest study on its fish oil-based Vascepa/Vazkepa CVD medication (icosapent ethyl, aka IPE), suggesting that IPE improves users’ coronary physiology — thus giving Amarin a new hemodynamic angle to support its previous findings that IPE reduces plaque and MACE.
With two FDA clearances and 20 million prescriptions so far, Vascepa has achieved quite a bit, but it hasn’t yet reached what some viewed as its early potential.
- Vascepa’s arguably slow start hasn’t been helped by follow-up analysis suggesting that IPE’s MACE reductions might not be as strong as initially presented in its 2018 REDUCE-IT trial.
- Amarin followed-up in 2020 with the EVAPORATE trial, which showed that IPE significantly reduced plaque burden among patients on statin therapy with known CAD, although REDUCE-IT still gets the most public attention.
The new EVAPORATE-FFRCT study looks to provide physiologic evidence to further support IPE’s REDUCE-IT trial results.
Researchers applied HeartFlow’s FFR-CT analysis to CTA imaging data from 47 IPE and placebo participants in the EVAPORATE trial (507 coronary lesions). The IPE group had similar average baseline FFR-CT values versus the placebo group (0.83 vs. 0.84), but showed…
- Significantly improved average FFR-CT values in the distal coronary segment in the most diseased vessel per patient at 9 months (0.01 vs. −0.05; P = 0.002) and 18 months (−0.01 vs. −0.09; P = 0.003) — the primary endpoint
- Statistically insignificant changes in translesional FFR-CT values (−0.06 vs. −0.09; P = 0.054) across the 140 most severe coronary lesion per vessel — the secondary endpoint
In other words, the EVAPORATE-FFRCT study demonstrated that IPE delivers significant, early, and sustained coronary physiology improvements, while providing mechanistic insights into the often-discussed results from the REDUCE-IT trial.
These results also highlight FFR-CT software’s potential for drug research and for assessing patients’ treatment response, noting that EVAPORATE-FFRCT is the first trial to use FFR-CT to determine the personalized effectiveness of CVD drugs.
The Takeaway
Although this new EVAPORATE-FFRCT data might not be enough to quiet Vascepa’s REDUCE-IT critics, it does provide solid evidence that IPE improves coronary physiology and could add more credibility to the results from its previous trials.
Perhaps more notable for readers who aren’t focused on Vascepa, this study could pave the way for a wider range of FFR-CT use cases, including drug research and assessing treatment responses.
|




|
|
Transformation Through Structured Reporting
Ready to realize the benefits of cardiovascular imaging structured reporting? Check out these quick and powerful Change Healthcare videos detailing the efficiency gains provided by structured reporting and what it takes to drive adoption.
|
|
Staging Coronary Artery Disease
Believe it or not, there’s been no clinically relevant atherosclerosis staging system used to characterize heart disease — until now. Check out Cleerly’s four-stage system for evaluating atherosclerotic plaque burden, which is the direct cause of coronary artery disease (CAD).
|
|
Creating A Novice Heart Failure Screening Pathway
We hear a lot about AI’s potential to expand echocardiography to far more users and clinical settings, and a study using Us2.ai’s AI-automated echo analysis and reporting solution showed that echo’s AI-driven expansion might go far beyond what many of us had in mind.
|
|
- Philips DCR’s PCI Impact: New data presented at EuroPCR 2023 showed that Philips’ Dynamic Coronary Roadmap (DCR) software significantly reduces contrast media use and total angiograms during PCI procedures. The DCR4Contrast trial randomized 371 patients to undergo PCI with or without Philips DCR navigation, finding that per procedure the DCR group used an average of 28.8% less contrast media and required 26.3% fewer angiograms.
- AHA Stress Research: The American Heart Association awarded $15M to research teams at Ohio State, UC Davis, and VCU who will study how stress affects cardiovascular health, and what interventions might reduce stress-related CVD risks. The studies will specifically look into: 1) If exercise can protect against stress-induced heart disease; 2) How stress from everyday life can impact heart health; and 3) How acute stress like receiving a cancer diagnosis may suddenly impact CV health.
- Angiogram Video AI: A UCSF-led team developed an AI model that uses coronary angiogram videos to detect patients with reduced LVEF (≤40%) and predict their LVEF percentage. When validated against internal and external datasets, the CathEF AI model somewhat accurately identified people with reduced LVEF (AUCs: 0.911 & 0.906), while its continuous LVEF predictions achieved 8.5% and 7.0% mean absolute error rates. However, the model tended to overestimate low LVEFs and underestimate high LVEFs.
- Postmenopausal Women’s AS Risks: New research presented at EACVI 2023 suggests that postmenopausal women with atherosclerosis have higher cardiovascular event risks than similarly aged men, and might need more intense lipid-lowering treatments. Analysis of 2k adults’ CCTAs and 3.7-year outcomes found that CCTA-based atherosclerosis burden was equally predictive of MACE among <55yr-old men and women, but women aged ≥55yrs had far higher risks of MACE than similar-aged men with the same atherosclerosis burden.
- Look out, ChatGPT: Google introduced its newest large language model, PaLM 2, which includes an updated Med-PaLM 2 version for healthcare. Google highlighted Med-PaLM 2’s “9x reduction in inaccurate reasoning” compared to the previous Med-PaLM model, its “expert” level performance answering questions from medical licensing exams, and ability to interpret medical images.
- BASILICA vs. Chimney Stenting: Data presented at EuroPCR found that BASILICA and chimney stenting are similarly effective for preventing coronary obstruction after TAVI, although BASILICA showed some advantages. Researchers analyzed 71 chimney patients and 97 BASILICA patients treated at hospitals that exclusively performed one of the two procedures. The chimney and BASILICA procedures had similar technical success rates (98.5% vs. 96.9%) and one-year MACE rates (18.7% vs. 19.9%), although chimney stenting had more complications and higher one-year CV mortality risks (6.7% vs. 1.3%).
- Robocath Unveils R-One+ Robotics Platform: French robotic cardiovascular surgery company Robocath unveiled its new R-One+ platform, which reportedly reduces radiation exposure and makes coronary angioplasty procedures safer, easier, and more precise. The R-One+ platform combines a robotic unit (robot and articulated support arm) and a command unit that interventional cardiologists can use in the cath lab or in a control room.
- Patients’ TOF Perspectives: A new JACC study supports using patient feedback, in addition to clinical metrics, to improve outcomes following tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) repair procedures. The observational trial of 607 adolescents and adults with repaired TOF found that patients’ reported quality of life scores were consistently good across age groups, but older patients reported lower perceived health statuses. Patients with the best self-reported outcomes were generally white, employed, nonsyndromic and asymptomatic, and had better LV function.
- Esaote’s New Portable Cardiac Ultrasound: Ultrasound vendor Esaote used last week’s EACVI 2023 meeting to debut its MyLab Omega eXP portable cardiac ultrasound. The Omega eXP sports new quantification features and uses CAAS Qardia software from Esaote’s Pie Medical Imaging group to automate echo measurements.
- Alirocumab FH Plaque Reductions: The ARCHITECT study found that the PCSK9 inhibitor alirocumab reduces coronary plaque burden and stabilizes plaque in asymptomatic patients with familial hypercholesterolemia on high-intensity statin therapy. In the phase IV trial, 104 patients received 150mg of alirocumab every 14 days, in addition to high-intensity statin therapy. After 78 weeks, the alirocumab/statin regimen led to a decline in plaque burden (from 34.6% to 30.4%), increases in calcified and fibrous plaque (+0.3% & +6.2%), and decreases in fibro-fatty and necrotic plaque (–3.9% & –0.6%).
- TeraRecon’s CV Visualization Update: ConcertAI’s TeraRecon announced the launch of Intuition 4.7, making a range of structural heart-targeted additions to the company’s flagship advanced visualization product. The new Intuition 4.7 release adds a new LAA workflow, an updated TMVR workflow, and various enhancements intended to streamline coronary imaging and pre-op planning.
|
|
PRECISE Trial Rewrites the Patient Pathway
HeartFlow’s landmark PRECISE trial found that their precision approach for evaluating people with stable chest pain avoided unnecessary testing and improved care without putting patients at risk of a missed heart disease diagnosis.
|
|
Monebo’s AF ECG Algorithm
Atrial fibrillation is often difficult to characterize with an automated algorithm due to the changing waveform morphology, system, or muscle noise. This is especially true given the size constraints of ambulatory devices to detect AFib. See how Monebo’s Kinetic AF ECG Algorithm overcomes these size limitations without sacrificing accuracy.
|
|
Relieving The Burden of Post-Processing
With the advent of advanced imaging technologies like CCTA come added burdens to technologists and diagnostic imaging centers. See how PIA can relieve the burden of post-processing, saving you time while helping your bottom line.
|
|
|
|
|