|
Improving Chest Pain Triage | Empagliflozin’s CKD Impact
January 26, 2023
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“I keep joking we’re going to have a big bonfire, and we’re going to take all those stethoscopes and burn them, because there aren’t many times a stethoscope helps us today.”
|
|
Emergency physician and point-of-care ultrasound pioneer, Diku Mandavia.
|
|
|
|
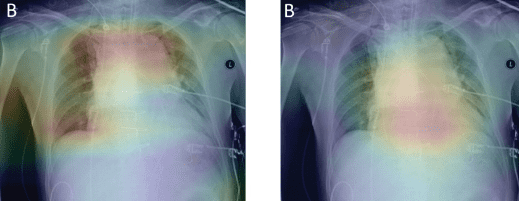
Patients who arrive at the ED with acute chest pain (ACP) syndrome end up receiving a series of often-negative tests, but a new MGB-led study suggests that incorporating AI-based chest X-ray (CXR) analysis might make ACP triage more accurate and efficient.
The researchers trained three ACP triage models using data from 23k MGH patients to predict acute coronary syndrome, pulmonary embolism, aortic dissection (the three cardiovascular causes of ACP), plus all-cause mortality within 30 days.
- Model 1: Patient age and sex
- Model 2: Patient age, sex, and troponin or D-dimer positivity
- Model 3: CXR AI predictions plus Model 2
In internal testing with 5.7k MGH patients, Model 3 predicted which patients would experience any of the ACP outcomes far more accurately than Models 2 and 1 (AUCs: 0.85 vs. 0.76 vs. 0.62), while maintaining performance across patient demographic groups.
- At a 99% sensitivity threshold, Model 3 would have allowed 14% of the patients to skip additional cardiovascular or pulmonary testing (vs. Model 2’s 2%).
In external validation with 22.8k Brigham and Women’s patients, poor AI generalizability caused Model 3’s performance to drop dramatically, while Models 2 and 1 maintained their performance (AUCs: 0.77 vs. 0.76 vs. 0.64). However, fine-tuning with BWH’s own images significantly improved the performance of the CXR AI model (from 0.67 to 0.74 AUCs) and Model 3 (from 0.77 to 0.81 AUCs).
- At a 99% sensitivity threshold, the fine-tuned Model 3 would have allowed 8% of BWH patients to skip additional cardiovascular or pulmonary testing (vs. Model 2’s 2%).
The Takeaway
Acute chest pain is among the most common reasons for ED visits, but it’s also a major driver of wasted ED time and resources, given that only 2% to 7.5% of patients are diagnosed with cardiovascular conditions covered by this triage model.
Considering that most ACP patients undergo CXR exams early in the triage process, this proof-of-concept study suggests that adding CXR AI could improve ACP diagnosis and significantly reduce downstream testing.
|




|
|
PRECISE Trial Rewrites the Patient Pathway
HeartFlow’s landmark PRECISE trial found that their precision approach for evaluating people with stable chest pain avoided unnecessary testing and improved care without putting patients at risk of a missed heart disease diagnosis.
|
|
Transformation Through Structured Reporting
Ready to realize the benefits of cardiovascular imaging structured reporting? Check out these quick and powerful Change Healthcare videos detailing the efficiency gains provided by structured reporting and what it takes to drive adoption.
|
|
- Empagliflozin Improves CKD: Results from the EMPA-KIDNEY trial revealed that the empagliflozin SGLT2 inhibitor improves chronic kidney disease outcomes. The researchers randomized 6.6k patients with CKD to receive empagliflozin (10 mg once daily) or a placebo, finding that the SGLT2 inhibitor group was associated with lower risk of kidney disease progression or cardiovascular death (13.1% vs. 16.9%; HR 0.72) and lower risk of all-cause hospitalization (HR: 0.86). Those results were consistent among patients with or without diabetes and across subgroups.
- Intermountain + Story Health: Less than a month after Intermountain teamed up with Omada to combine in-person and virtual care for diabetes patients, the Utah-based health system announced a similar partnership with Story Health to improve access to specialty care for patients with heart failure. The partnership combines Intermountain’s in-person cardiovascular expertise with Story Health’s virtual care platform / health coaches to personalize treatments and engage patients as they carry out their care plans.
- ChatGPT Authoring Research: It didn’t take long for the AI world’s latest poster child, ChatGPT, to make its formal debut in scientific literature, and it’s already notched at least four authorship credits on published papers and preprints. As you might imagine, many scientists disapprove of the chatbot’s growing role as a research co-author, and publishers are now scrambling to regulate its use.
- CMRI’s Dark-Paps Marker: Italian researchers discovered a new cardiac MRI marker, called Dark-Paps (dark papillary muscles), that can help detect higher-risk patients with ventricular arrhythmias and LV preserved ejection fraction. After testing various LV papillary muscle features, they found that patients with end-systolic signal hypointensity of both papillary muscles in early post-contrast cine CMR images (aka Dark-Paps) had higher cardiac event risks over seven years (p < 0.0001). Adding Dark-Paps also improved the performance of other predictive models based on late gadolinium enhancement and non-sustained ventricular tachycardia.
- Cardiac Arrests During Sports: Truveta performed a timely analysis of its patient dataset following the on-field collapse of Buffalo Bills safety Damar Hamlin, finding that about 9.92 cardiac arrests occur for every 100k sports injuries that result in a hospital visit. The incidents were most often associated with basketball, with fewer related to football, baseball, and soccer. Although less than one cardiac arrest occurred for every 10k injuries since 2016, it’s worth noting that Truveta only reported on injuries that led to ED or inpatient encounters.
- HVR Cardio Secures $11.1M: Clinical stage medical device startup HVR Cardio secured $11.1M in Series B funding to help advance transcatheter mitral valve repair with its CathHELIX Annuloplasty System, which is used to treat mitral regurgitation. The funding will let HVR Cardio begin human clinical trials on the CathHELIX as it looks to prove that it’s a safe and effective way to reduce MR without tethering the native leaflets.
- Could Ultrasound Replace the Stethoscope? The New Yorker revived the “handheld ultrasound will replace the stethoscope” storyline, detailing how technological and clinical advancements are bringing ultrasounds into new settings, potentially at the expense of the iconic stethoscope. The author highlighted handheld ultrasounds’ growing list of advantages (small, low-cost, no radiation, accurate, flexible, point-of-care accessible), while suggesting that recent progress in training, adoption, AI assistance, and telemedicine could make it a go-to device for a broad range of clinical settings – including in some patients’ homes.
- Sac/Val Switchers’ Angioedema Risks: A JACC study revealed that patients switching to Sacubitril-Valsartan (SV) from ACE inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) have higher risk angioedema. The propensity score–matched cohort study showed that SV users who switched from ACE inhibitors and ARBs within 183 or 14 days had notably higher angioedema risks than new SV patients (ACE-to-SV HRs: 1.62 & 1.98; ARB-to-SV HRs: 2.03 & 2.45). However, new SV users had the same angioedema risks as new ACE inhibitor and ARB users.
- No AI Education: The calls for AI education appear to be growing louder, after a STAT article suggested that med schools are “missing the mark” on artificial intelligence training. The article argued that med schools’ lacking AI curriculums are creating knowledge gaps that might hinder future physicians’ ability to spot AI mistakes, compounding the damage caused by flawed algorithms and biased decision-support systems.
- Phlox Therapeutics + Solid Biosciences: Dutch biotech firm Phlox Therapeutics is teaming up with Solid Biosciences to develop novel precision genetic medicines for a severe form of genetic dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) for which there is currently a significant unmet need for effective treatments. The collaboration integrates Solid’s vector biology, manufacturing capabilities, and drug development experience with Phlox’s expertise in genetic cardiomyopathies and RNA therapeutics.
|
|
Us2.ai’s Echo Evidence
Have more echo studies than sonographers? See how Us2.ai was able to classify, segment, and annotate echocardiographic videos with similar accuracy as expert sonographers.
|
|
How Precision Heart Therapy Advances the Business of Healthcare
Health systems continue to face economic and regulatory pressure to reduce care costs and improve outcomes. See how Cleerly’s precision heart care approach helps enhance patient care, avoid unnecessary and high-cost procedures, and improve the patient and provider experience.
|
|
PIA’s Post-Processing Solution
Advanced cardiac imaging often calls for a time-consuming post-processing step, requiring costly software, hardware, and training. See how PIA provides this post-processing at lower cost, improved consistency, and greater efficiency.
|
|
|
|
|