|
Medtronic’s Defibrillation Innovation | ESC Study Drop
September 2, 2022
|
|
|

|
|
Together with
|

|
|
|
“One must merely sew. And when one knows where to sew, there is no problem.”
|
|
Åke Senning (1915-2000), on performing the first heart transplant in Switzerland in 1969. Iconic.
|
|
|
Surgeries & Interventions
|
|
|
|
|
|
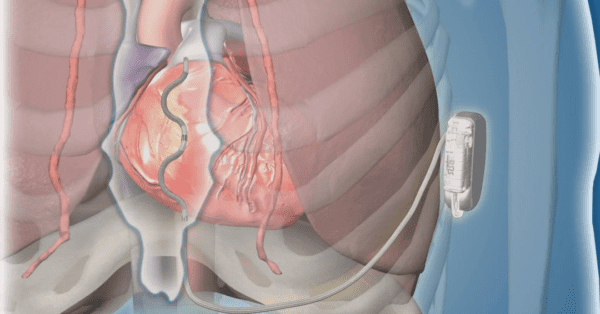
A new era of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be on the horizon. In this premarket clinical study, Medtronic’s unique extravascular ICD effectively terminated acute and chronic life-threatening arrhythmias, while simultaneously hitting safety endpoints.
In contrast to traditional ICD leads which are inserted through veins into the heart, this device’s lead is placed directly behind the sternum and connected to a device implanted below the patient’s left armpit. By placing the lead beneath the breastbone but outside of the heart, the team reduced risks associated with transvenous ICDs such as lung collapse, heart perforation, and heart valve damage.
In the prospective single-group study of patients with a class I or IIa indication for an ICD, 316 participants underwent an attempted implant, and 299 were discharged with a working extravascular ICD system.
- Physicians successfully terminated an induced ventricular arrhythmia in 298 of 302 patients (98.7%).
- At six months, 92.6% of participants had no major system or procedure-related complications.
- Out of 18 recorded episodes of cardiac arrest, 100% were converted back to normal heart rhythms after delivering shocks.
- 23 patients experienced major complications, the most common being dislodgement of the lead wire.
- 29 patients experienced inappropriate shocks, at an average of 10.6 months after implantation, with most linked to over-sensing of the heart’s electrical signals.
The Takeaway
Overall, researchers found that the EV ICD achieved a defibrillation success rate of 98.7%—the original goal was 88%—and met all safety endpoints. Medtronic has received a green light from the FDA to continue studying the device while the agency reviews its premarket application.
|




|
|
Staging Coronary Artery Disease
Believe it or not, there’s been no clinically relevant atherosclerosis staging system used to characterize heart disease — until now. Check out Cleerly’s four-stage system for evaluating atherosclerotic plaque burden, which is the direct cause of coronary artery disease (CAD).
|
|
Automating the Fight Against Heart Disease
See how Us2.ai cuts echocardiography’s manual work, subjectivity, and turnaround times to automate the fight against heart disease.
|
|
- Women’s Higher AFib Risk: Challenging conventional wisdom, a new study of 26k CVD-free subjects demonstrated that women have a 50% *higher* risk of developing AFib than men when height and weight are accounted for. While men had a higher risk of AFib when researchers adjusted for typical risk factors (BMI, age, smoking, alcohol intake, etc), the association flipped when researchers substituted height and weight for BMI in the multivariate model (hazard ratio: 1.5, median follow-up: 5.3 yrs). This suggests that differences between male and female body sizes account for much of the protective association between being female and AFib.
- Medtronic Acquires Affera: Medtronic completed its $1B acquisition of cardiac arrhythmia solutions company Affera, marking Medtronic’s expansion into the cardiac mapping and navigation space. Affera’s suite of technologies (including the Prism-1 heart mapping software, the Sphere-9 cardiac diagnostic & ablation catheter, and the Sphere PVI ablation catheter) will complement Medtronic’s existing arrhythmia management portfolio.
- P2Y12 Monotherapy Bests Aspirin: A meta-analysis of 35.7k patients found that P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy was associated with a lower risk of ischemic events than aspirin monotherapy in patients with coronary artery disease. Researchers compared data from 12k patients on P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy and 12k patients on aspirin monotherapy (median treatment: 557 days) and found that CV death, MI, or stroke was less likely to occur in the P2Y12 inhibitor group (5.5% vs. 6.3%). The P2Y12 inhibitor group also experienced fewer GI bleeds (hazard ratio: 0.75).
- AliveCor & Dignio Team Up: Personal ECG company AliveCor has teamed up with Dignio UK to integrate its KardiaMobile device into the MyDignio smartphone app. AFib patients participating in the Leicester NHS Trust’s virtual ward project will now be able to record their own ECGs remotely and send the results directly to clinicians.
- Cardioneuroablation for Fainting: A randomized study found that adults with recurrent vasovagal syncope had fewer events and improved quality of life (QoL) when they underwent cardioneuroablation. Researchers randomized 48 patients with recurrent reflex asystolic syncope into cardioneuroablation (CNA) and non-pharmacological treatment groups. At two years, only 8% of CNA receivers experienced syncope recurrence, compared with 54% in the control group. Over the same time period, the CNA group’s QoL score improved by 67%, while the control group’s score remained the same.
- Amgen’s LDL Medication: An ESC-presented study found that long-term LDL cholesterol lowering with evolocumab (Amgen’s Repatha) was safe, well tolerated, and led to sustained reductions in CV events. In the study, 6.6k adults with ASCVD received placebo or evolocumab (either 140mg every two weeks or 420mg monthly) and were followed for a median of 5 years. Evolocumab was tied to a 58% LDL-C reduction long-term, and 80% of evolocumab receivers achieved an LDL-C level under 55mg/dL by week 12.
- Hospital Margins in for a Rough Q4: July’s hospital margin update from Kaufman Hall is in, and frankly, the results are bleak. Median operating margins plummeted to -0.98%, revenue dropped 4.8%, and labor expenses climbed 3.5% since June. Persistent labor shortages and a growing number of patients choosing ambulatory centers for surgical procedures helped reverse any margin gains made in recent months, causing Kaufman Hall to warn health systems not to lose sight of long-term capital planning despite the urgency of day-to-day pressures.
- Bayer’s Sudden Cardiac Death Drug: Fresh data revealed that Bayer’s drug Kerendia (finerenone) significantly reduced sudden cardiac death among patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes. Researchers pooled data from 13k patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes and found that the Kerendia patients had an 18% reduced risk of all-cause and CV mortality, and a 25% lower risk of sudden cardiac death. Kerendia received FDA approval last July to treat CKD associated with type 2 diabetes, and is in its second year of a phase 3 trial for HFpEF.
- Echo AI Superiority: A Cedars-Sinai team developed and tested an ultrasound AI system that was able to measure cardiac function more effectively than veteran sonographers (14yr avg. tenure). Cedars-Sinai cardiologists evaluated 3,495 transthoracic echo ejection fraction reports that were either generated by AI or sonographers, making corrections to a smaller share of the AI-based reports than the sonographer reports (16.8% vs. 27.2%) and finding that AI ejection fraction readings were closer to actual EF measurements (2.8 vs. 3.8 avg. pct point variation).
- Nighttime Dosing: A large, randomized trial concluded that taking blood pressure medication in the evening is not better than taking it in the morning. Researchers randomized 21k patients with high blood pressure into either a morning or evening dosing group. Over a 5.2-year median follow-up, the evening and morning groups experienced hospitalization for nonfatal myocardial infarction or nonfatal stroke, or vascular death, at similar rates (3.4% vs. 3.7%).
- BC VFA, a CVD Risk Marker: A new AJR study highlighted automated CT-based body composition (BC) analysis’ potential to identify patients with high visceral fat area (VFA) and greater risks of future cardiovascular events. Using routine abdominal CTs from 9,752 patients and an automated AI-based BC analysis system, the researchers produced three automated BC measurements (skeletal muscle area, subcutaneous fat area, and VFA), finding that patients with the highest VFA measurements had greater future risks of heart attack and stroke than patients with the lowest VFAs (hazard ratios: 1.31 & 1.46).
|
|
Detecting CAC and Undiagnosed CAD
Do you know how many patients in your health system are at risk for coronary artery disease but are undiagnosed? This article details how Nanox AI’s CAC solution can help clinicians identify those who often go undetected.
|
|
|
|
|